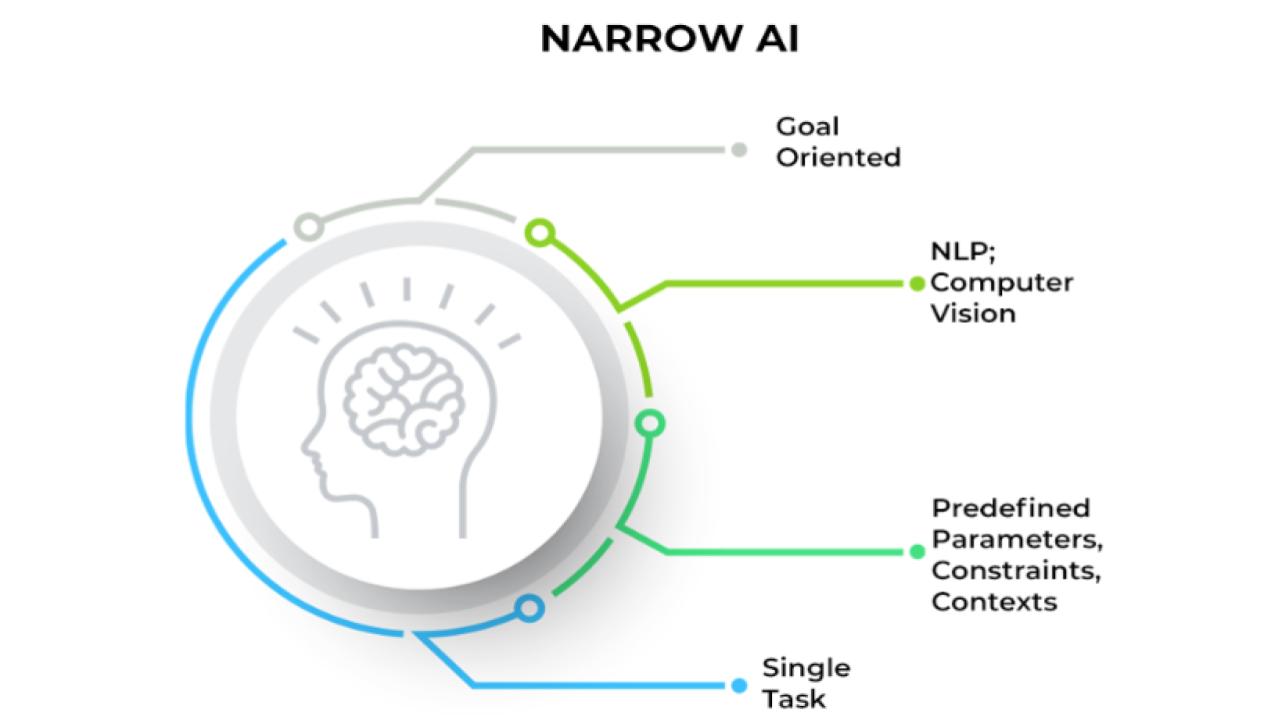
Narrow AI can be classified as being “limited to a single, narrowly defined task. Most modern AI systems would be classified in this category.” Artificial general intelligence is conversely the opposite.
- Definition:
ANI is AI designed to perform a specific task or solve a narrowly defined problem.
- Examples:
Virtual assistants like Siri and Alexa, facial recognition systems, recommendation engines, and chatbots.
- Limitations:
ANI lacks general cognitive abilities and cannot learn beyond its programmed capabilities.
- Current Status:
ANI is the type of AI that exists and is widely used today.
OnAir Post: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI)